Have you ever received an email attachment with a strange file extension and thought, “What on earth is this?” Or struggled to choose the right format when saving your work? You’re not alone. In today’s digital workplace, understanding file types is essential for smooth communication and professional efficiency.
Whether you’re sending a resume, sharing a logo, or presenting data to stakeholders, picking the right file format can make the difference between a polished professional impression and a frustrating technical hiccup.
Why Understanding Different Types of Files Makes You More Effective
In our digital-first world, knowing the right file formats isn’t just technical knowledge; it’s a career superpower. Understanding the landscape of digital formats helps you avoid frustrating moments like sending a document your client can’t open or uploading an image that cripples your website’s loading speed.
Here’s why mastering file formats matters in real-world scenarios:
✨ Smoother Collaboration
Colleagues, clients, and vendors use different tools. Sending a .pages file to a Windows user or a .heic A photo of someone on Android creates unnecessary friction. Choosing universally compatible formats prevents back-and-forth emails and missed deadlines.
✨ Professional Polish
A pixelated logo on your website? A resume that reformats itself on the hiring manager’s screen? These small-format mistakes silently undermine your credibility. Selecting the right file type ensures your work looks exactly as intended every time.
✨ Time and Storage Savings
A 20MB TIFF photo might look stunning, but it’s overkill for an email signature. A 500MB MOV video won’t upload smoothly to social media. Smart format choices help you balance quality with practicality, saving bandwidth, storage space, and loading time.
✨ Future-Proofing Your Work
Today’s cutting-edge format (like AVIF for images) becomes tomorrow’s standard. Staying aware of evolving file types keeps your digital assets relevant and compatible as technology advances.
✨ Security Awareness
Not all formats are safe to open. Executable files (.exe) from unknown sources pose risks, while password-protected archives (.zip, .rar) add layers of security. Format knowledge helps you navigate digital safety with confidence.
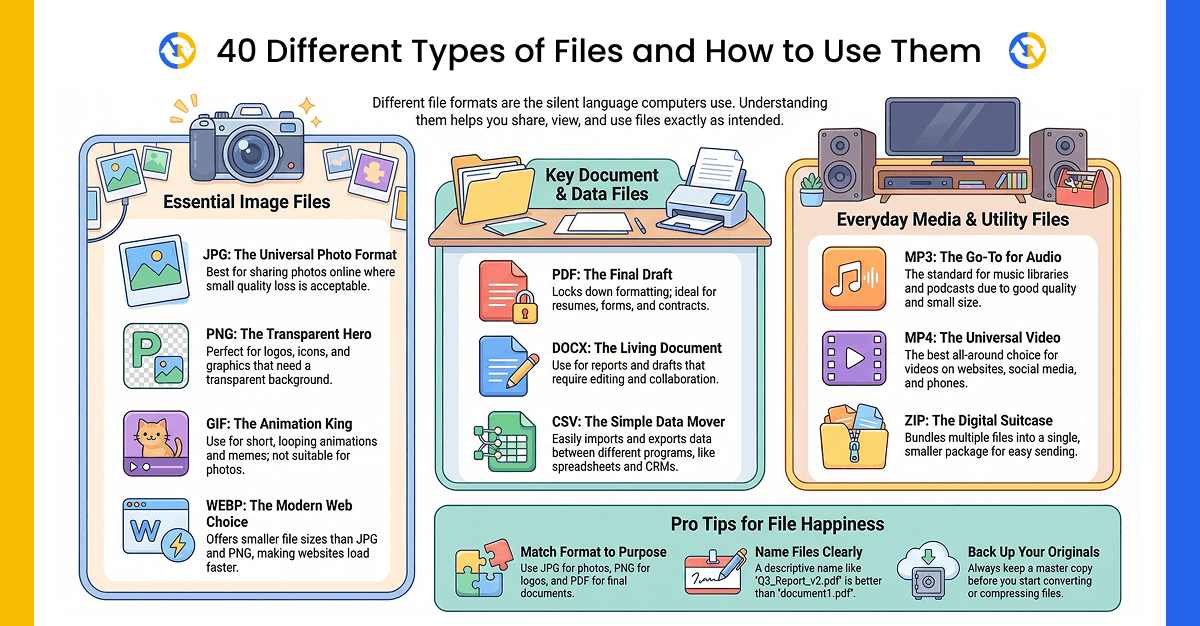
Let’s dive into 40 essential file types you’ll encounter in your career and learn exactly when and why to use each one.
📄 Document File Formats (7 Types)
1. PDF (Portable Document Format)
The universal standard for sharing documents should look identical on any device. Perfect for:
- Resumes and cover letters
- Contracts and legal documents
- Reports and presentations for distribution
- Forms that need to maintain layout
Pro Tip: Need to convert a document to PDF? Tools like FileToConvert.com make it quick and easy.
2. DOC / DOCX (Microsoft Word Document)
The go-to format for editable text documents. DOCX is the modern version with better compression and recovery features. Use for:
- Drafting and editing reports
- Collaborative writing projects
- Resumes when specifically requested by employers
- Documents requiring track changes and comments
3. ODT (OpenDocument Text)
An open-source alternative to DOCX, commonly used with LibreOffice and OpenOffice. Ideal for:
- Organizations using free office suites
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Privacy-focused workflows
4. HTML / HTM (Hypertext Markup Language)
The foundation of web pages. Essential for:
- Web developers and content creators
- Email marketing templates
- Online documentation
- Blog posts and articles
5. XLS / XLSX (Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet)
Industry standard for data management and analysis. Perfect for:
- Financial reports and budgets
- Data tracking and metrics
- Charts and graphs
- Contact lists and databases
6. TXT (Text File)
Simple, unformatted text that opens everywhere. Use for:
- Basic notes and instructions
- Code snippets
- Plain text emails
- When you need universal compatibility
7. CSV (Comma-Separated Values)
Tabular data in plain text format. Essential for:
- Importing/exporting data between systems
- Email marketing lists
- Database migrations
- Spreadsheet data exchange
🖼️ Image File Formats (10 Types)
8. JPEG / JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
The most common photo format. Great for:
- Website images and social media posts
- Email attachments with size constraints
- Digital photography sharing
- When file size matters more than perfect quality
⚠️ Note: JPEG uses lossy compression—repeatedly saving the same file degrades quality over time.
9. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
Lossless compression with transparency support. Use for:
- Logos with transparent backgrounds
- Screenshots and technical diagrams
- Graphics requiring sharp edges
- Web images where quality is a priority
10. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
The original animated image format. Perfect for:
- Short looping animations
- Memes and reaction images
- Simple graphics with limited colors
- Lightweight website elements
11. SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
Vector-based format that scales infinitely without quality loss. Ideal for:
- Logos and icons
- Website graphics that need resizing
- Illustrations and diagrams
- Search engine-friendly graphics
12. TIFF / TIF (Tagged Image File Format)
High-quality format for professional use. Best for:
- Print publications and marketing materials
- Scanned documents requiring archival quality
- Professional photography masters
- When file size isn’t a concern
13. WebP
Google’s modern format offers superior compression. Perfect for:
- Website optimization (smaller files, faster loading)
- Modern web projects
- When you need both quality and efficiency
14. BMP (Bitmap)
Uncompressed raster format. Use sparingly for:
- Windows system graphics
- When absolutely no compression is acceptable
- Legacy software compatibility
15. HEIC / HEIF (High Efficiency Image Format)
Apple’s space-saving photo format was introduced with iOS 11. Great for:
- iPhone photo storage (smaller files, same quality)
- Modern photo libraries
- When working in Apple ecosystems
⚠️ Challenge: Limited compatibility with Windows—often needs conversion for sharing.
16. ICO (Icon)
Windows-specific format for application icons and favicons. Use for:
- Desktop application icons
- Website favicons (browser tabs)
- Small graphics (16×16 to 256×256 pixels)
17. AVIF (AV1 Image File Format)
The next-generation image format with incredible compression. Perfect for:
- Cutting-edge web projects
- When you need the smallest file sizes with the best quality
- Future-proofing your digital assets
🎨 Design & Creative File Formats (4 Types)
18. PSD (Photoshop Document)
Adobe Photoshop’s native format preserves layers and editing capabilities. Use for:
- Photo editing projects
- Digital art and illustrations
- Web design mockups
- When you need non-destructive editing
19. AI (Adobe Illustrator Artwork)
Vector graphics format for scalable illustrations. Ideal for:
- Logo design and branding
- Illustrations and infographics
- Print materials requiring scalability
- Professional graphic design work
20. EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
Legacy vector format is still used in printing. Perfect for:
- Print industry workflows
- Logo files for printers
- Cross-software vector compatibility
- When clients request this specific format
21. RAW
Unprocessed camera sensor data. Essential for:
- Professional photography
- Maximum editing flexibility
- Preserving original image data
- When quality is non-negotiable
🎥 Video File Formats (6 Types)
22. MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14)
The universal video format. Compatible with virtually everything. Use for:
- Social media video content
- Website video embedding
- Email attachments (when size allows)
- Mobile device compatibility
23. MOV (QuickTime Movie)
Apple’s high-quality format. Ideal for:
- Professional video editing on Mac
- Training videos and presentations
- When working in Apple ecosystems
- High-quality video exports
24. AVI (Audio Video Interleave)
Microsoft’s older format with good quality. Suitable for:
- Windows-based video editing
- When maintaining quality through multiple edits
- Legacy system compatibility
- Simple video sharing
25. MKV (Matroska Video)
Flexible container supporting multiple tracks. Great for:
- Videos with multiple audio/subtitle options
- Archival purposes
- When you need all-in-one video packages
- High-definition content storage
26. WebM
Open-source format optimized for the web. Use for:
- HTML5 video embedding
- Modern website video content
- When you want a royalty-free format
- Browser-based video streaming
27. FLV (Flash Video Format)
Designed for streaming (though Flash is now obsolete). Still used for:
- Legacy website video players
- When a small file size is critical
- Older streaming platform uploads
🔊 Audio File Formats (3 Types)
28. MP3 (MPEG Layer Audio 3)
The universal audio format. Perfect for:
- Music libraries and playlists
- Podcast distribution
- Voice memos and recordings
- Maximum compatibility across devices
29. WAV (Waveform Audio File)
Uncompressed, studio-quality audio. Ideal for:
- Professional audio recording
- Music production and editing
- When quality is more important than file size
- Windows-based audio work
30. M4A (MPEG-4 Audio)
Compressed audio with good quality. Use for:
- Podcast episodes
- Voice recordings and lectures
- When you need smaller file sizes
- iTunes and iOS compatibility
📢 Presentation File Formats (3 Types)
31. PPT / PPTX (PowerPoint Presentation)
The industry standard for business presentations. Perfect for:
- Client pitches and sales presentations
- Training sessions and workshops
- Board meetings and stakeholder updates
- When you need animations and transitions
32. ODP (OpenDocument Presentation)
Open-source alternative for LibreOffice/OpenOffice users. Ideal for:
- Organizations using free office suites
- Cross-platform presentation sharing
- Privacy-conscious environments
- Collaborative presentation work
33. KEY (Apple Keynote)
Apple’s sleek presentation format. Best for:
- Mac-based presentation creation
- When working with the Apple ecosystem
- Beautiful, design-focused presentations
- Modern slide design aesthetics
📦 Compressed & Archive File Formats (4 Types)
34. ZIP
The most widely supported compression format. Use for:
- Bundling multiple files for email
- Reducing file sizes for transfer
- Creating backups
- Universal compatibility
35. RAR (Roshal Archive)
Better compression than ZIP. Perfect for:
- Large file distributions
- When you need stronger compression
- Password-protected archives
- Software distribution
36. 7Z (7-Zip)
Advanced compression with encryption options. Ideal for:
- Maximum file size reduction
- Secure, encrypted archives
- Long-term storage optimization
- When you have 7-Zip software available
37. ISO (Disc Image)
Exact copy of optical discs (CD/DVD/Blu-ray). Use for:
- Operating system installations
- Software distribution
- Disc backups and archiving
- Virtual machine setups
💻 System & Special File Formats (3 Types)
38. EXE (Executable)
Windows program files. ⚠️ Caution: Only open from trusted sources—common malware carrier. Use for:
- Installing software on Windows
- Running applications
- System utilities and tools
39. DMG (Disk Image)
macOS installer and disk image format. Perfect for:
- Mac software installations
- Creating bootable drives
- Disk backups on Mac systems
- Distributing Mac applications
40. DLL (Dynamic Link Library)
Windows system files contain code and data. ⚠️ Technical: Don’t modify unless you know what you’re doing. Used for:
- Windows operating system functions
- Software component sharing
- System-level programming
💡 Pro Tips for Choosing the Right Format
For Job Applications
- Resumes: PDF (unless employer specifies DOCX)
- Portfolios: PDF or website links
- Cover Letters: Match the resume format
For Business Communication
- Reports: PDF for distribution, DOCX for editing
- Data: XLSX for analysis, CSV for sharing
- Presentations: PPTX for editing, PDF for final distribution
For Marketing & Web
- Images: WebP or JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with transparency
- Videos: MP4 for universal compatibility
- Logos: SVG for websites, PNG for documents
For Archival & Quality
- Photos: TIFF for masters, JPEG for distribution
- Audio: WAV for editing, MP3 for sharing
- Documents: PDF/A for long-term preservation
🔄 When You Need to Convert File Formats
Sometimes you’ll receive a file in an incompatible format or need to change formats for a specific purpose. Common conversion needs include:
- HEIC to JPG: iPhone photos for Windows users
- DOCX to PDF: Finalizing documents for distribution
- PNG to WebP: Optimizing website images
- Gif to PNG/JPG: Sharing design mockups with clients
For quick, reliable file conversions without installing software, check out FileToConvert.com, your go-to solution for seamless format transformations.
Even with all this knowledge, you’ll still encounter moments when a file arrives in the wrong format, like iPhone HEIC photos that won’t open on Windows or a client requesting a PDF instead of a DOCX. That’s where FileToConvert.com saves the day: a fast, secure, and free online tool that handles 300+ format conversions in seconds no software installation required. Whether you’re converting HEIC to JPG, DOCX to PDF, or PNG to WebP, simply upload, convert, and download. Your perfect format is just one click away.